最近剛用 python django 寫了一個經典的縮網址服務,並且使用 django-allauth 套件實作 Google 以及 Facebook 登入。
在開發以及過程中遭遇到一些問題,這邊主要記錄一些我印象深刻的問題。
# 克服 Django-allauth 開發問題
# App 簡介
這個 app 希望有以下功能:
- 使用者可以使用 Google or Facebook 登入。
- 登入後可以建立縮網址。
- 縮網址可以前往原本的網址。
- 使用者可以看到自己縮網址的點擊成效。
後端我主要使用以下套件
- django: python web framework
- django-allauth: 與 django 搭配的 auth 套件,可以用來實作第三方登入
- django-rest-framework: 開發 django restful api 的套件
- drf-spectacular: 產生 openAPI yaml 作為 API 文件
- django-decouple: 讀取 .env file 的環境變數
- celery: 非同步執行,用以加快回應速度
前端則是參考 django-allauth spa 官方範例,使用 react 開發。
原始碼可以參考 GitHub
# 開發遇到的問題
# 1. CSRF Token Missing
剛開始開發第三方登入時遇到一個嚴重的問題,因為 django-allauth 會使用 django csrf middleware 作為驗證,所以所有非安全的 http 請求都要帶 csrf token。我有兩種方式取得 csrf token,第一是從 django 產生的頁面中找到帶有 csrfmiddlewaretoken 的元素,第二就是在 django server 的某些請求的回應中會帶有 set-cookies。
因為我採用 spa 的開發模式,所以無法直接從 django 產生的頁面拿到 csrftoken。而在 react 中頁面一開啟都會打 /_allauth//_allauth/browser/v1/config 而這個 endpoint 回傳都會在 set-cookies header 帶 csrftoken。本來以為在這樣的狀況下,只要從 docuement.cookie 就可以達到 csrftoken,沒想到事情沒有那麼簡單。
原因在於在開發環境,我的前端 host 是 localhost:3000,但是後端是 localhost:8000,這不符合 cookie 的 same site,所以前端無法從 document.cookie 得到 csrftoken。我在參考 cookie 的 secure, same site, httpOnly 等的設定後,幾經修改都無法讓前端順利拿到 csrftoken,於是我直接在開發環境使用 traefik 作為 reverse proxy,這樣在基本的 django 設定之下我就可以成功在前端拿到 csrftoken,畢竟在通過 reverse proxy 之後,這就算是同一個網站了。原本 reverse proxy 是想要在部署時才使用的,現在就在開發時一併使用。
# 2. OAuth2 Redirect URL Mismatch
2-1 Redirect Url Settings
Facebook 還有 Google 的 OAuth2 都有 redirect_url 的參數,這可以告知 OAuth2 server 當驗證完之後要將請求導回到 app。而這個 redirect_url 需要事先從開發者 console 設定,這邊的說明跳過如何建立 app,已經有很多教學文了。
Facebook (2025-01)
- 從 developer 頁面 進入
My Apps- 點擊要設定的 app
- 左側選單中選擇
Use Cases- 找到要設定的功能(我這邊是Authenticate and request data from users with Facebook Login),點擊 Customize。
- 進入功能設定頁面後,左側在 permissions 底下有 settings,點擊 settings
- 進入 OAuth client 設定,可以在這邊設定並且驗證 redirect_url。
Google (2025-01)
- 從 Google Auth Platform Clients 頁面
- 點擊要設定的 client id
- 進入頁面即可在設定頁面左下角找到 redirect_url 的設定區域
在開發時我依照 django-allauth 文件,將 redirect 設定為 http://localhost:10000/accounts/{provider}/login/callback/。若是沒有設定,或者 redirect_url 與後台的設定不相符,會出現 OAuth2 server 會回傳 400 http status code。
在設定完之後,我的 app 就可以使用 Google 或者 Facebook 登入了。
2-2 Reverse Proxy Settings
開發的時候一切都好,不過當我部署到對外伺服器的時候又發生問題了。
我使用我自己家中的舊電腦做伺服器,上面已經使用了 nginx 作為 reverse proxy,我打算將 url shortener 也掛在 nginx 後面,整體會像下圖:
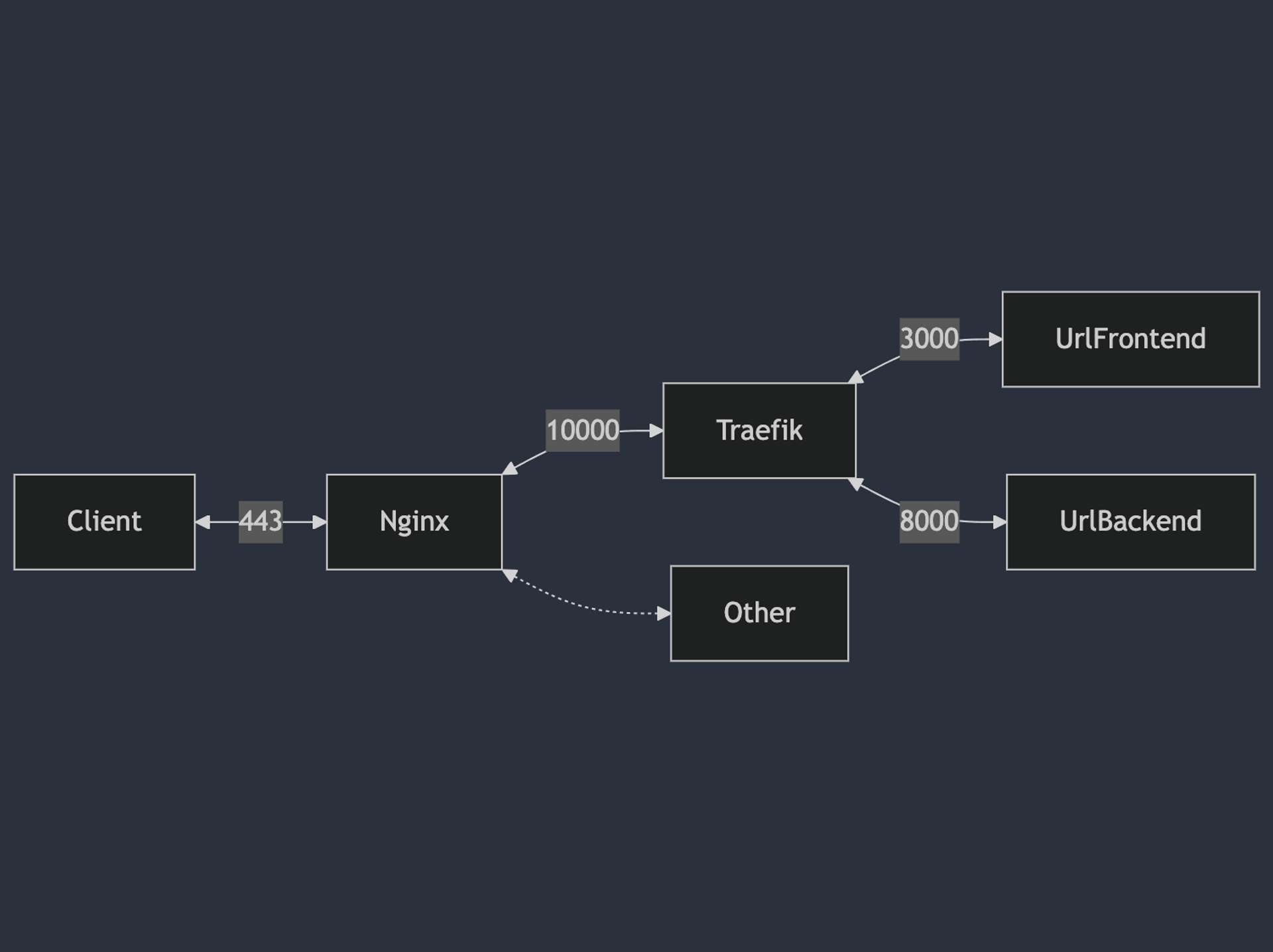
當我把所有服務都使用 docker compose 架好,並且設定好 nginx reverse proxy 之後,當我嘗試使用第三方登入時,我又出現 redirect_url mismatch 了。我細看錯誤訊息,發現 redirect_url 被設定為 http://localhost:10000/account/provider/callback,而不是我網站的 domain。
我當下覺得應該是 nginx 有問題,在查找了各式資料以及問過 AI 之後,我找到問題來源,主要原因是使用 reverse proxy。
使用 reverse proxy,當 request 經過 proxyt 時會被再一次送出,而這個過程中部分 request header 會改變,包含辨識 host 的 header。
但是這些 header 的改變又與 redirect_url 有什麼關係?這就要去看 django-allauth 的 source code。
django-allauth 使用第三方的流程大致上是對自己的 api /_allauth/browser/v1/auth/provider/redirect 發送 post request,而 view 就會依照 request payload 產生 redirect_url 等第三方登入需要的 payload,然後回傳 302 將使用者導向第三方驗證頁面。
可以參照 django-allauth/utils.py#L285
def build_absolute_uri(request, location, protocol=None):
"""request.build_absolute_uri() helper
Like request.build_absolute_uri, but gracefully handling
the case where request is None.
"""
from .account import app_settings as account_settings
if request is None:
if not app_settings.SITES_ENABLED:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
"Passing `request=None` requires `sites` to be enabled."
)
from django.contrib.sites.models import Site
site = Site.objects.get_current()
bits = urlsplit(location)
if not (bits.scheme and bits.netloc):
uri = "{proto}://{domain}{url}".format(
proto=account_settings.DEFAULT_HTTP_PROTOCOL,
domain=site.domain,
url=location,
)
else:
uri = location
else:
uri = request.build_absolute_uri(location) # THIS LINE
# NOTE: We only force a protocol if we are instructed to do so
# (via the `protocol` parameter, or, if the default is set to
# HTTPS. The latter keeps compatibility with the debatable use
# case of running your site under both HTTP and HTTPS, where one
# would want to make sure HTTPS links end up in password reset
# mails even while they were initiated on an HTTP password reset
# form.
if not protocol and account_settings.DEFAULT_HTTP_PROTOCOL == "https":
protocol = account_settings.DEFAULT_HTTP_PROTOCOL
# (end NOTE)
if protocol:
uri = protocol + ":" + uri.partition(":")[2]
return uriL285 uri 一般狀況會是用 request 的 method。而這個 request 是 django HttpRequest,這邊就可以看 django/http/request.py#L148
class HttpRequest:
### other properties
def _get_raw_host(self):
"""
Return the HTTP host using the environment or request headers. Skip
allowed hosts protection, so may return an insecure host.
"""
# We try three options, in order of decreasing preference.
if settings.USE_X_FORWARDED_HOST and ("HTTP_X_FORWARDED_HOST" in self.META):
host = self.META["HTTP_X_FORWARDED_HOST"]
elif "HTTP_HOST" in self.META:
host = self.META["HTTP_HOST"]
else:
# Reconstruct the host using the algorithm from PEP 333.
host = self.META["SERVER_NAME"]
server_port = self.get_port()
if server_port != ("443" if self.is_secure() else "80"):
host = "%s:%s" % (host, server_port)
return host
可以看到 request 會根據條件去判斷使用 X-Forwarded-Host, Http-Host, Server-Name 其中一個作為 host 去組成 absolute url。在這邊因為我是在 reverse proxy 的環境中部署,根據文件要在 django 設定 USE_X_FORWARDED_HOST = True。
所以我先設定好 django,並且在我的 nginx.conf 中把 headers 設定好。
nginx.conf
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name my.short.url;
ssl_certificate /data/short.url.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /data/short.url.key;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:10000;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header Http-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}不過當我設定好了之後,我的 redirect_url domain 依舊是 localhost,在核對 nginx 以及 django 設定之後,我轉向 traefik 去確認可能的問題在哪裡。在這邊我找到traefik entry points forwarded headers 設定,這邊我先使用設定 insecure mode,注意,這不是推薦的用法,正確用法是要設定好 proxy trusted ips,否則會有潛在資安問題。
traefik.toml
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":10000"
# use this in a secure reverse proxy environment
[entryPoints.web.forwardedHeaders]
insecure = true
當我再次點擊要登入,又出現 redirect_url mismatch,仔細看這次 domain 對了,不過 redirect_url 的 protocol 是 http,但是我在後台設定的是 https,依舊不一樣。而這裡則又要回去看 django request 是怎麼取得 scheme, django/http/request.py#L290
class HttpRequest:
### other properties
def scheme(self):
if settings.SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER:
try:
header, secure_value = settings.SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER
except ValueError:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
"The SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER setting must be a tuple containing "
"two values."
)
header_value = self.META.get(header)
if header_value is not None:
header_value, *_ = header_value.split(",", 1)
return "https" if header_value.strip() == secure_value else "http"
return self._get_scheme() # return "http"可以看到如果沒有設定 SECURE_PROXY_SSL_HEADER 或者設定不正確,就只會回傳 http,這邊也是回頭找 django 文件,在這邊設定好 header 的 key, value,並且再去設定 nginx.conf
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name my.short.url;
ssl_certificate /data/short.url.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /data/short.url.key;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:10000;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header Http-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; # add this line
}
}在設定完這些之後,我終於可以在我的縮網服務使用第三方登入!
# 結語
這些問題是我在開發上花最多時間解決的問題,雖然有些問題自己追到後面發現文件已經寫了要怎麼設定,不過我自己是還滿喜歡這樣追原始碼搞清楚他們到底在做什麼的。
關於作者
我是好人