嗨,我是 Cian。
最近意外成為了一個前後端各半的半半工程師,這篇文章和大家分享最近研究 gRPC 的成果。
# 首先, RPC 是什麼?
RPC 是 Remote Procedure Calls (遠端程序呼叫)的簡稱。
簡單來說,RPC 是一種調用遠端程序的模式。它讓我們在使用遠端的 Procedure 的時候,可以像使用 local 調用一樣方便。
Client 和 Server 都會有一個 Stub(樁),這個 Stub 會把底下的處理抽象化,因此對於 Client 端來說,他是和 Stub 互動,並不會在意他使用的這個函數實際上寫在哪。
因為可以像是調用本地函式一樣調用遠端函式,這個模式解决了分布式系統中 Server 間的調用問題。
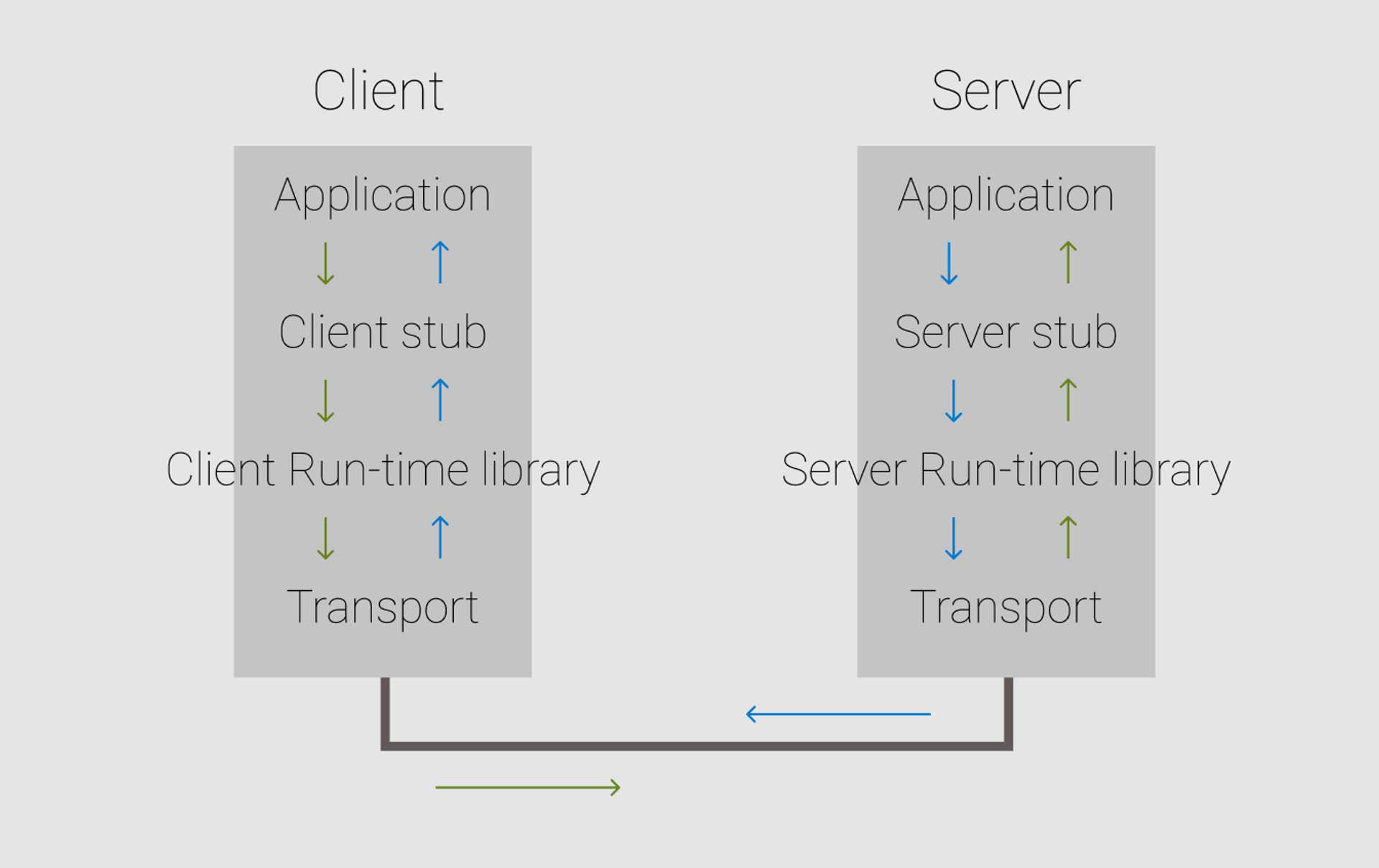
這張圖簡單描述了整個 RPC 的過程:
- Client 的 Application 是這個 Procedure 的調用,他會調用 Client Stub 中的 Method
- Client Stub 是一個把調用過程包裝起來的代理對象,他其實並不擁有 Client Application 想要調用的 Method,所以他會向外進行 RPC 的調用。
- Client Run-time Library 是一個實現 RPC 調用的工具包
- 最後我們會透過底層網路實現 data 的傳輸。
# gRPC
接著,來看一下 gRPC 是什麼。
gRPC(Remote Procedure Calls)是 Google 發起的一個開源的 RPC 系統。目標是讓我們可以更輕鬆地創建分佈式應用程序和服務。

gRPC 基於 HTTP/2 協定傳輸,並且使用 Protocol Buffers 作為介面描述語言(IDL)。
使用 gRPC 的流程如下:
- 在一個
.proto的 Protocol Buffers 檔案中定義想要的數據類型和方法 - 使用 gRPC 的 CLI 指令進行編譯
- 在編譯之後,會根據這個文件生成 Stub 的 Interface,以及一些的 Accessors(訪問器)
- 透過實現這些 Interface 和 Accessors,我們可以輕鬆地用各種語言在各種數據流中讀寫結構化數據
gRPC Client 和 Server 可以在各種環境中運行及進行通信,而且可以自由選用支援 gRPC 的語言進行開發。舉上圖的例子來說,我們可以在 Server 端,以 C++ 開發 gRPC Server,並且在 Client 端同時選用 Ruby 和 Android Java 來開發。
另外由於他有嚴格的 API 規範,因此也十分適合團隊使用。
在這中間,因為只是想調用一下遠端的 Procedure,所以 RPC 其實常常選用傳輸效率更高的二進制傳輸,過程中會有序列化和反序列化的部分。
# Protocol Buffers
gRPC 預設的 IDL 是 Protocol Buffers,雖然其實也可以使用像是 JSON 等其他數據格式,但當然最推薦使用的就是這個 IDL。它是一種序列化結構化數據。
Protocol Buffers 的官網上是這樣介紹自己的:
Protocol buffers are Google's language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data – think XML, but smaller, faster, and simpler.
簡單翻譯是「Protocol Buffers 是 Google 的語言原生、平台原生的可擴張機制。用於序列化結構化的 data。有點像是 XML,但更小、更快也更簡單。」
Protocol Buffers 適合用在高性能,對響應速度有要求的數據傳輸場景。因為它以二進制傳輸,所以數據本身不具有可讀性。我們會需要透過反序列化之後得到真正可讀的數據。
# gRPC 的四種生命週期
受惠於它基於 HTTP2 的技術,gRPC 支援四種生命週期,可供不同的使用場景選用:
Unary:一對一
一個 request 對上一個 response
Client-side streaming: 多對一
Client 送很多個請求(Streaming),結束之後 server 只回一個 response
Server-side streaming:一對多
Client 只上傳一個請求,但 Server 回一堆 response(Streaming)
Bidirectional streaming:多對多
Client 和 Server 都以 Streaming 的形式交互# 實作 Unary
作為練習,我們實作一個 Unary 的 gRPC 系統。目標是 Client 給定一個座標,Server 會返回對應的景點名。
# install
首先,今天要嘗試寫的是 Go 的 gRPC。
需要,先到 ~/go/src 底下建立一個這次專案的資料夾,這裡叫它 grpc/ 。
接著安裝 grpc。
$ go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@v1.26
$ go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@v1.1和更新 PATH
$ export PATH="$PATH:$(go env GOPATH)/bin"- 這一段請以官網內容優先:Quick start | Go | gRPC
# 定義 Protocol Buffers 檔案
在 ~/go/src/ 底下新增一個 grpc/ 資料夾作為我們這次的專案資料夾。
新增一個 route.proto 檔案。
首先,定義要回傳的 message 類型,我們想回傳的是一個位置情報,會有這個地點的名字和他的座標。
// route.proto
/* 指定使用的是 proto3 的語法 */
syntax = 'proto3';
option go_package = ".;route";
/* option 不會改變聲明的整體含義,但可能會影響它在特定上下文中的處理方式 */
package route;
/* 定義要回傳的 message 類型,我們想回傳的是一個位置情報 */
/* 座標訊息 */
message Point {
int32 latitude = 1; // 把一個數字作為key使用,可以壓縮長度。要從 1 開始。
int32 longitude = 2;
}
/* 相關訊息 */
message Feature {
string name = 1;
Point location = 2;
}接著,定義要進行回傳的方法 GetFeature,他會接收一個座標情報,並且回傳這個座標上的景點訊息。
// route.proto
service RouteGuide {
// Unary
rpc GetFeature(Point) returns (Feature) {}
}# go.mod
我們會需要一個 go.mod 檔案來描述我們的專案將使用的 modules,不然後期可能會遇到引入問題。
module route
go 1.16
require (
google.golang.org/grpc v1.38.0
google.golang.org/protobuf v1.26.0
)# 生成 stub code
接著,我們使用官方提供的指令產生 route.pb 文件和 route_grpc.pb 兩個文件。
我們這裡使用 go。
$ protoc --go_out=. --go_opt=paths=source_relative --go-grpc_out=. --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative route.proto- 可能會遇到「Please specify a program using absolute path or make sure the program is available in your PATH system variable --go_out: protoc-gen-go: Plugin failed with status code 1.」error,可以嘗試
go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@latest指令,詳情參考 這篇文章 ,對我有效。
在剛剛的指令完成之後,我們在 route.pb.go 檔案中會找到我們定義的 message 的 struct:
type Point struct {
// ...
Latitude int32 `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=latitude,proto3" json:"latitude,omitempty"` // 把一個數字作為key使用,可以壓縮長度。要從 1 開始。
Longitude int32 `protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=longitude,proto3" json:"longitude,omitempty"`
}
和
type Feature struct {
//...
Name string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name,proto3" json:"name,omitempty"`
Location *Point `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=location,proto3" json:"location,omitempty"`
}
接著我們也可以在 route_grpc.pb 文件中找到一些 gRPC 生成的 Interface
Server
// RouteGuideServer is the server API for RouteGuide service.
// ...
type RouteGuideServer interface {
// Unary
GetFeature(context.Context, *Point) (*Feature, error)
mustEmbedUnimplementedRouteGuideServer()
}以及 Client
// RouteGuideClient is the client API for RouteGuide service.
// ...
type RouteGuideClient interface {
// Unary
GetFeature(ctx context.Context, in *Point, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*Feature, error)
}接下來,我們要分別在 Client 和 Server 把其中的方法實踐出來。
# Client
這裡我們先寫 Client。
Client 的目標是發送一個 Point type 的值並且取得該座標的景點情報。
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
pb "route/route"
)
func main() {
conn,err := grpc.Dial("localhost:5000",grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBlock())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := pb.NewRouteGuideClient(conn)
feature,err := client.GetFeature(
context.Background(),
&pb.Point{
Latitude: 353931000,
Longitude: 139444400,
},
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
fmt.Println(feature)
}Dial 是 grpc 提供的一個方法,會是一個 dail 請求,第一個參數會說他要播向哪裡,之後是一些 option。grpc.WithInsecure():因為現在 server 端沒有提供驗證,所以使用 Insecure 來跳過驗證grpc.WithBlock():如果沒有成功就不讓他往下走的一個選項
NewRouteGuideClient 是 grpc 自動生成在 Client stub 產生的一個方法,可以在 route_grpc.go 找到它的定義,不過總之他會接收一個連接的 Interface,並且回傳一個 RouteGuideClient 類型的東西。
在製作時,會有像這樣的 suggest,調用 Server 的 GetFeature 就像是調用 local 的 method 一樣方便。
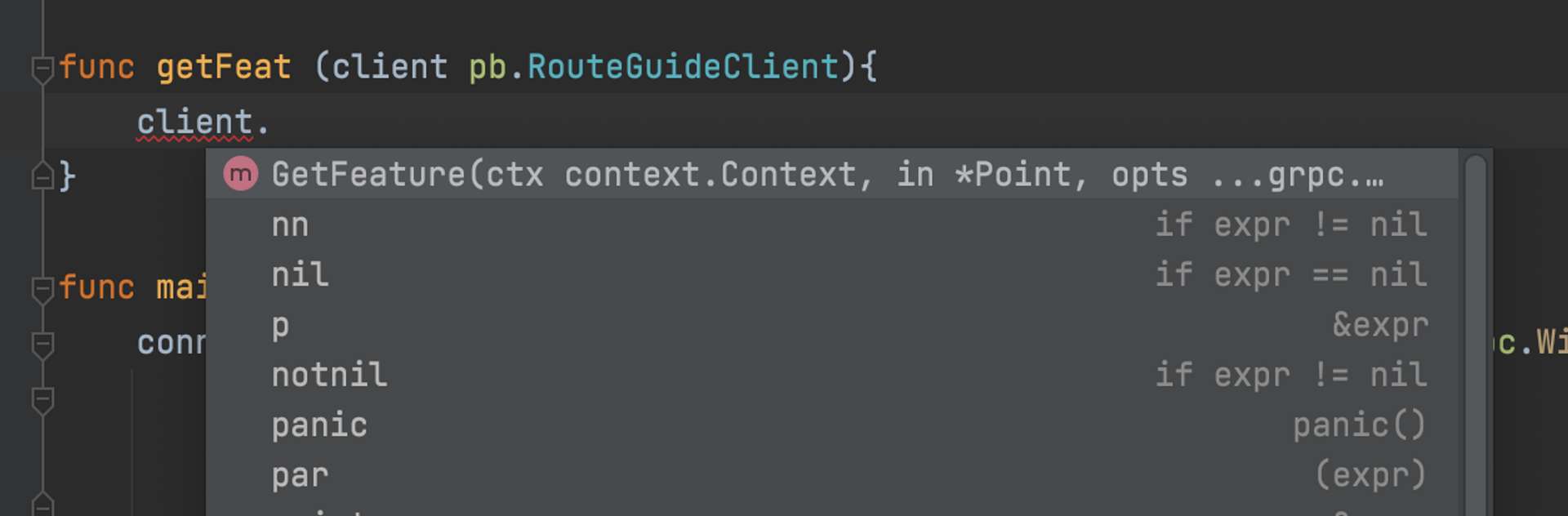
RouteGuideClient 是我們定義的方法的 Interface,我們可以調用 Interface 中指定好的 GetFeature 。
這時真正在做這個處理的是 Server 端,所以我們開始實踐 Server 端吧!
# Server Side
這部分要做的事情有:
- 製作資料庫(optional)
- 資料處理
- 開一個 Listener 監聽 request
# 資料庫
這裡我們做一個開發用的簡易 DB。
在 route/ 資料夾旁邊生成一個 route-server/ 資料夾,並新增一個 server.go 檔案,我們要在這裡實現 Server stub 的 interface。
首先,定義 routeGuideServer 的 type
// server.go
package main
import (
pb "route/route" // 透過 `proto` 生成的 Server Stub
)
type routeGuideServer struct {
pb.UnimplementedRouteGuideServer
}在這裡,因為在這個 routeGuideServer interface 中有一個 mustEmbedUnimplementedRouteGuideServer(),所以必須要有這個東西,是用來實現向上兼容的。
接著我們先做 Server 的假 DB 部分。
在這個 routeGuideServer 中,加上這一行 DB 的 type 定義。
type routeGuideServer struct {
pb.UnimplementedRouteGuideServer
features []*pb.Feature
}我們把這個 DB 叫做 features,裡面是有個一些 feature 的 Slice。
// server.go
func dbServer() *routeGuideServer {
return &routeGuideServer{
features: []*pb.Feature{
{
Name: "東京鐵塔",
Location: &pb.Point {
Latitude: 353931000,
Longitude: 139444400,
},
},
{
Name: "淺草寺",
Location: &pb.Point {
Latitude: 357147651,
Longitude: 139794466,
},
},
{
Name: "晴空塔",
Location: &pb.Point {
Latitude: 357100670,
Longitude: 139808511,
},
},
},
}
}# 資料處理
有了資料就可以開始處理了。
這個 Server 的目標是在收到一個 request 時回傳回相對應的景點資訊,在這裡我們先簡單使用 for loop 遍歷進行比對,並回傳合適的資料。
也就是作出 API 中的 GetFeature(context.Context, *Point) (*Feature, error) 的實體:
// server.go
// import 要加上這兩個 Library
import (
pb "route/route"
"context" // 新增
"google.golang.org/protobuf/proto" // 新增
)
func (s *routeGuideServer) GetFeature(cxt context.Context, point *pb.Point) (*pb.Feature, error){
for _,feature := range s.features{
if proto.Equal(feature.Location, point){
return feature, nil
}
}
return nil, nil
}# Listener
最後是在 main 中開一個 Listener 監聽,如果沒有問題,就使用 gRPC 內建的 Server 來進行處理。
到這裡的 import 區
import (
"log" // 新增
"net" // 新增
"context"
pb "route/route"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/proto"
"google.golang.org/grpc" // 新增 grpc library
)接著寫 main()
func main() {
// 生成一個listener
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", "localhost:5000")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("cannot create a listener a the address")
}
// server
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterRouteGuideServer(grpcServer, dbServer())
log.Fatalln(grpcServer.Serve(lis))
}使用 net.Listen 生成一個 listener 之後,使用 grpc.NewServer() 產生一個 grpcServer,接著向 grpc 把這個 Server 登記在案。
之後就使用 grpcServer.Serve(lis) 來取得 Listener 拿到的資訊,就可以了。
兩邊都跑跑看,結果就會像這樣。
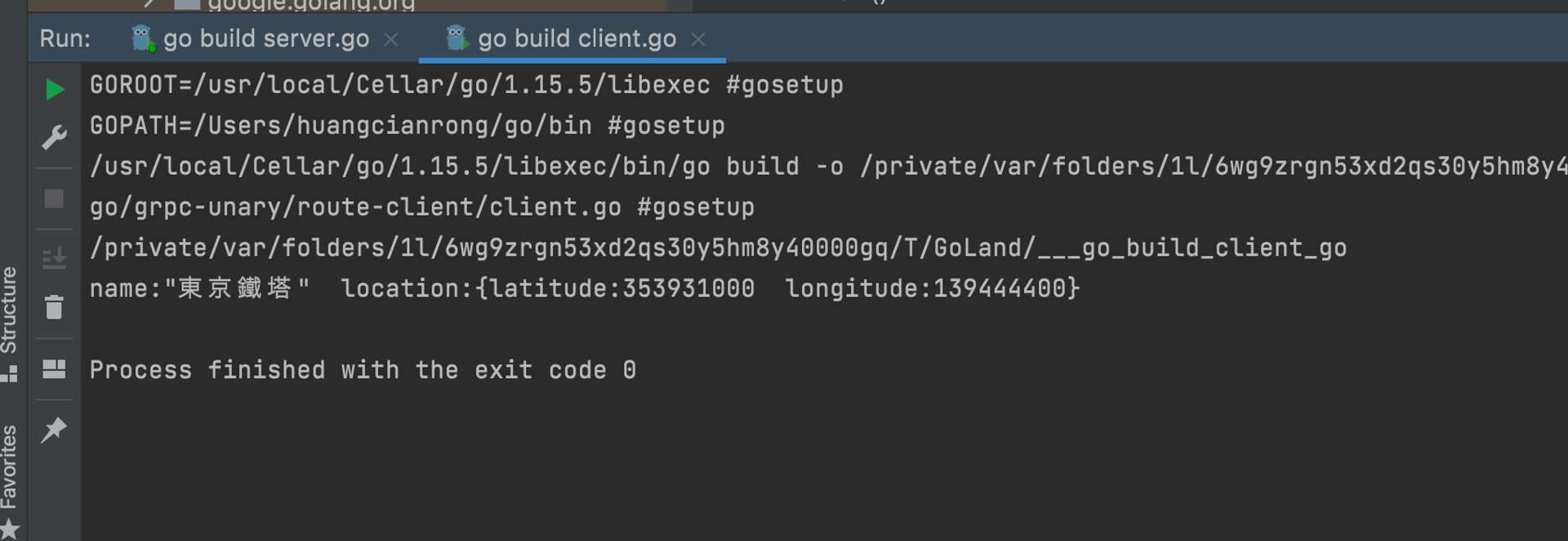
到這裡就做到了簡單的 Unary,完成可以連接的前後端。
# 重構
因為之後需要再開其他 api ,所以這裡先把 Unary 的相關處理放到函式 getFeat 裡面。
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
pb "github.com/keronscribe/learn-go/grpc-unary/route"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
)
func getFeat (client pb.RouteGuideClient){
feature,err := client.GetFeature(context.Background(),&pb.Point{
Latitude: 353931000,
Longitude: 139444400,
})
if err != nil{
log.Fatalln()
}
fmt.Println(feature)
}
func main () {
conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:5000", grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBlock())
if err != nil{
log.Fatalln("Client cannot dail grpc server")
}
defer conn.Close()
client := pb.NewRouteGuideClient(conn)
getFeat(client)
}
今天就到這裡,下一篇文章會繼續嘗試剩下三種生命週期。
# 參考資料
Introduction to gRPC | gRPC
Language Guide (proto3) | Protocol Buffers | Google Developers
Basics tutorial | Go | gRPC
Day20-Go modules - iT 邦幫忙
神奇代码在哪里Go实战#9:gRPC
「 gRPC Web 」で gRPC 実践! Go と gRPC で WebAPI を作ってみよう!!
同步刊載於個人部落格 使用 Golang 建立一個 gRPC 架構
關於作者
遊走在各種覺得有趣的知識之間。